Gravitational Wave Generator
Background Theory
Foamy Ether Theory describes electromagnetic waves as distortions in the foam that are transverse to the direction of propagation. When two electromagnetic waves, traveling in opposite directions meet, a compression of foamy ether (space) takes place between the waves.
Screen captures of a simulation (using ThreeDimSim) of this compression is illustrated in figures below. Figures 1a to 1f show how the foamy ether is distorted by an array of four antenna pairs that are fed phase shifted EM waves. The top red bar is a cross section of four antenna elements where the RF signal is flowing towards the viewer, while the bottom red bar has the RF signal flowing away from the viewer. Figure 1a shows the beginning of the distortion created by the first antenna pair; followed by Figures 1b to 1d. Figures 1e to 1f show how the compression wave continues to travel to the right even after the EM waves have completed their vertical distortions. This compression wave is equivalent to a Gravitational Wave (GW). (Notice that no compression wave leaves the left side of the antenna array).
Figure 2 shows the full simulation of three EM pulses creating three GW pulses.

Figure 1a Antenna 1 Pulse

Figure 1d Antenna 4 Pulse

Figure 1b Antenna 2 Pulse

Figure 1e
GW Exits Antenna Array

Figure 1c Antenna 3 Pulse
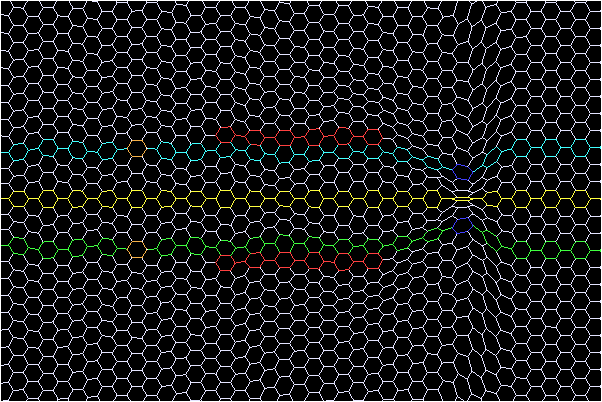
Figure 1f
GW Continues
Figure 2 Simulation of three EM pulses creating three GW pulses
A full description of the invention of a Gravitational Wave Generator V7 can be found on preprint server:
https://vixra.org/abs/2412.0056
And on my ResearchGate page:

